Mongolia


1. Activities (2010- )
| Month/ Year | Places (Prefecture, etc.) | Activities |
| 2024/11/26 | Tsukuba    |
The participants visited a water treatment plant, a sake brewery, and a soy sauce brewery in the Kasumigaura Lake region to explore the potential of biotechnology in advancing a sustainable society. During the internship, they learned how biological processes are applied and managed. They also gained insight into agrotourism by studying the rich history of sake and soy sauce fermentation, discovering how these traditions are deeply intertwined with Japanese culture and Have contributed to the local community. |
| 2024/08/10-08/14 | Shanghai (China)    |
From August 10 to 11, the students attended the International Conference on Bioprocess and Sustainability 2024 (ICBS2024) organized by Shanghai Academy of Environmental Sciences, Tongji University, Shanghai University, Tsinghua University, Nankai University, Hainan University and University of Tsukuba. In this conference the students had a good communication with the 18 invited professors and about 300 participants on the advancements of biological processes and their contributions to sustainable development goals (SDGs). In the following three days, the students firstly visited Shanghai Mengqing Theme Park where they acquired the history of water pollution, sewage collection, and management in Shanghai. During the visit to Shanghai Bailonggang Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP), the largest WWTP in Asia, the students learned how this largest WWTP treats about one-third of the sewage and sludge produced in Shanghai and gradually improves its sustainability. In Shanghai Qingpu Agricultural Park, they deeply understood how the local farmers environmentally friendly manage their farmland including irrigation system and agricultural wastes with improved crop productivity and quality in the context of SDGs. |
| 2024/07/30-08/01 | Tohoku    |
The participants visited disaster remains and museums in Miyagi and Iwate Prefectures to learn about the actual damage caused by the earthquake and tsunami of the Great East Japan Earthquake. The participants visited the Matsushima Coast and learned about the importance of tourism resources in the recovery process. Furthermore, they learned about the differences in disaster prevention efforts among various countries. |
| 2024/02/26 | Saitama & Tochigi   |
The participants visited the Metropolitan Area Outer Discharge Channel, which is designed to reduce flood disasters in the upstream areas from the Edo River to the Tone River. They collected information and exchanged views about its functions, effectiveness and costs about this world’s largest underground flood management facility. They also visited Watase Artificial Wetland, a Ramsar site, to gather information and exchange views about flood control, water supply, history of copper poisoning incident, wetland ecosystem and the role of annual controlled burning practices. |
| 2024/02/19-02/22 | Taiwan      |
The filed study promoted international exchanges for r different disciplines, especially integrated solid waste management, material science, technology innovation for small island economy, and ways to meet sustainable development goals through the collaboration of industry, educational institutions, and local community members. Participants learned from different green technology institutes at Feng Chai University especially related to bioplastics and GIS. They also learned about international platform for biotechnology professionals to share technologies and research achievements through collaboration to develop relevant technologies in the bioenergy sector. |
| 2024/01/31 | Tokyo   |
The participants visited areas in and around Tokyo to learn about flood and disaster preparedness and exchange views. In Tokyo, the participants gathered information about super levees along the Sumida River and the disaster prevention measures. Shioiri Park is located on the super levee that is designed for the evacuation site with emergency camp sites. They also visited Tokyo Rinkai Disaster Prevention Park in Tokyo Bay to experience disaster measures within 72 hours. Regarding private sector disaster management measure, they observed newly established Azabudai Hills. |
| 2023/12/02, 12/8 | TSUKUBA, Research Institute     |
Tsukuba and received on-site explanations from Dr. Tanaka, an expert on the impact of climate change on beech forests in the area (2 Dec). At the National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management (NILIM), the participants received training on sediment disasters and their countermeasures from Dr. Yamakoshi Director of the Erosion Control Research Office, and toured the experimental facilities. ibid. (8 Dec.). This enabled us to comprehensively enhance our knowledge on climate change issues from three perspectives: forecasting, natural effects (ecosystems) and social effects (disasters). |
| 2023/09/11-09/19 | Netherlands and Germany     |
JDS students visited the cities of Amsterdam and The Hague to discuss the problems posed by climate change, flooding and other disasters to urban functions. They gathered information from discussions with city officials on how to restore canals while preserving their own traditional canal landscapes and on the latest methods of waste disposal in canals. They also visited disaster prevention facilities to protect economic facilities on major rivers from flooding and sea level rise and learnt more about unique technologies. At the same time, information was collected on how to deal with groundwater chlorination. In Delft, they were informed about a sustainable innovation project at the University of Technology called Green Village, which is created from community-industry partnerships, and the development of a geothermal power plant on campus. In addition, they attended a lecture and exchanged views with a representative at the office of the water board, the Netherlands' own water resources management organisation since the Middle Ages. In Rotterdam, information was collected on traditional Dutch water measures. They also visited a floating office and a community project on urban greening and collected information on urban planning while observing the redevelopment of water landscapes. In addition, they visited recycling case studies to hear local opinions. At the Rhine River Commission in Koblenz, researchers from the organisation provided detailed information on the transboundary management system for the entire Rhine River. In Düsseldorf, they visited one of the largest urban greening projects in Germany and saw how trees in huge buildings are managed. Overall, the JDS students gained information on Dutch and German cutting-edge attempts in water management and climate change and urban and rural development, and were able to compare them with examples from their own countries and seek solutions to their own problems. |
| 2023/09/13-09/15 | Osaki Town (Kagoshima)   The length of the text is adjustable |
The participants visited Osaki Town, Kagoshima Prefecture, to learn about thorough resource recycling and circular society (i.e., the Osaki System), which Osaki has progressed through close collaboration among the municipal government, residents, and private companies under their original concept of Circular Village. During the field trip, they visited the final disposal site, organic and non-organic waste recycling facilities, local community waste collection, shochu (distilled spirit) factory, and eel farm. We also had special lectures by local experts from Osaki Town Office and Osaki SDGs Promotion Council. On the last day, the participants presented the characteristics of the Osaki System and the applicability of the system to their home countries. They discussed this with the local experts. |
| 2023/09/10-09/12 | Miyagi and Iwate   |
Participants visited ruins and museums related to the Great East Japan Earthquake in Miyagi and Iwate Prefectures, where they learned about the actual impact of earthquakes and tsunami disasters. They observed the distinctive geographical features of the Tohoku region's Pacific coastal area, which contribute to the expansion of tsunami damage in coastal areas. They also visited Tohoku University and attended a special lecture on the role of the ocean in disasters and abnormal weather. Participants engaged in discussions and exchanged opinions on disaster prevention challenges in various countries around the world. |
| 2023/02/11-02/18 | Kansai (Kyoto・Osaka・Kobe)  |
From February 11 to 18, 2023, the participants attended lectures by three researchers from Kyoto University and Kobe University, and learned academic and practical knowledge on water environment management, wastewater/waste treatment and resource recovery and biomass energy production, organic and smart agriculture through visits to Lake Biwa Museum, Yagi Bioecology Center, Wazuka Town, Kyoto University Graduate School of Agriculture Farm, Lake Biwa/Yodo River Water Quality Conservation Organization, Kobe City Higashinada Treatment Plant and Yuge Farm. Through visits to the Kyoto Graduate School of Agriculture farm, the Lake Biwa-Yodo Water Quality Conservation Organization, the Kobe Higashinada Treatment Plant, and the Yumigake Farm, participants acquired academic and practical knowledge about water environment management, wastewater/waste treatment/resource recovery and biomass energy production, organic farming and smart farming. Finally, through group work and presentations, students gained a deeper understanding of sustainable water environment management, agriculture, and environmental conservation. |
| 2023/01/31-02/03 | Amamiohsima (Kagoshima)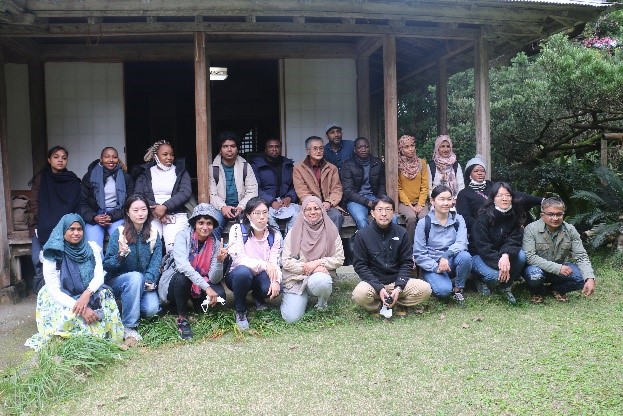   |
The JDS students visited Amami Oshima Island, which will be registered as a World Heritage site in 2021, to gather information and exchange views on the conflict between biodiversity conservation and regional development, the ideal form of ecotourism, future utilization of World Heritage natural resources, and disaster prevention measures in the region. The JDS students first learned about endangered and invasive species on Amami Oshima from local experts. Based on this, they participated in ecotourism through a certification program for guides. At the same time, they learned how to sustain the nature conservation required by the World Heritage registration from the construction administration-oriented economy that has continued for many years since the end of World War II. Furthermore, they gained the ability to analyze how disaster prevention measures due to global warming and typhoons are related to the sustainability of the local economy and environment. |
| 2023/01/25 | Kasaikaihin park・Tokyominatorie・Asakusa・Shioiri park (Tokyo)   |
In this activity, the group visited a Ramsar site in Tokyo to observe species conservation and public access. They also visited a museum to obtain an overall picture of the history of Tokyo's bayfront development and disaster prevention. Furthermore, to learn about the Tokyo Metropolitan Government's disaster prevention activities in the Sumida River basin, they visited super levees, bridges, and disaster prevention equipment to gather information and exchange views on countermeasures against urban disasters. This enabled the JDS students to examine the future of disaster prevention measures in their own countries by comparing them with examples from their own countries. |
| 2022/12/07-12/09 | Kitakyusyu (Hukuoka)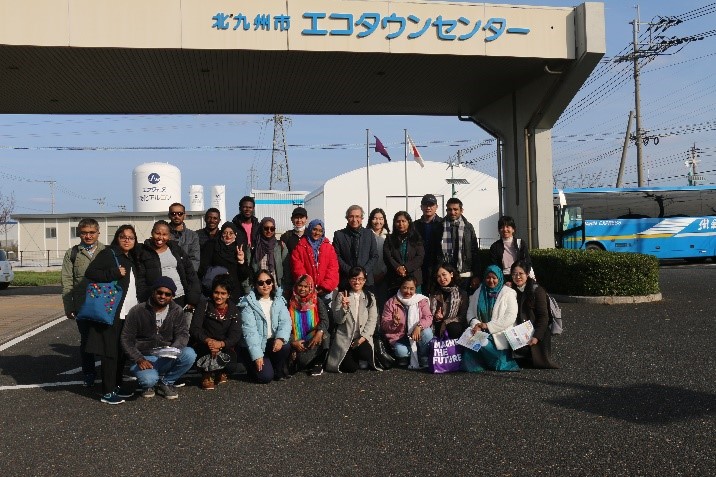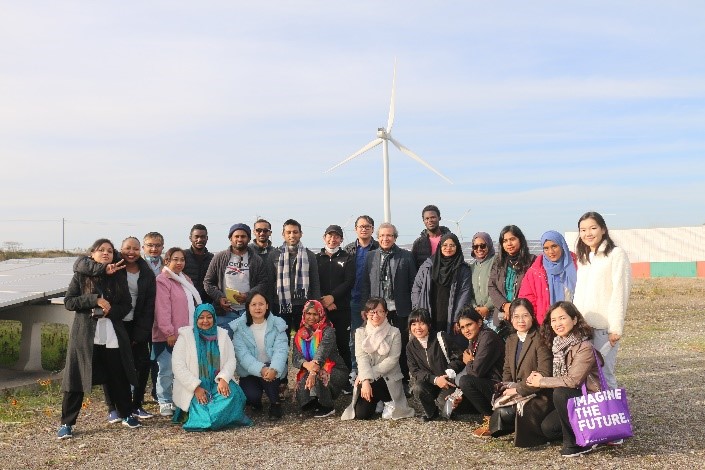   |
During this field study, we visited Kitakyushu Eco-Town and learned about the importance of cooperation between industry, government, and the city. Here, the students learned about recycling technologies for plastic bottles and e-waste. They also learned about wind and solar power generation systems in the Eco-Town complex. They also visited Yamaguchi Dairy's biogas plant, which produces biogas from by-products and waste from the dairy industry and uses it as an energy source for the industry. Finally, the students visited an incineration and resource recovery facility in Shimonoseki City. The students were able to understand the importance of having a life cycle thinking about resource management. |
| 2022/12/06 | Metropolitan Area Outer Discharge Channel (Saitama) and Watarase Wetland (Tochigi)    |
The participants visited the Metropolitan Area Outer Discharge Channel in Saitama Prefecture and Watarase Wetland in border areas of Tochigi, Ibaraki, Gunma, and Saitama prefectures. This training focused on flood control and wetland management in the Kanto region. At the Outer Discharge Channel, the JDS students visited the world's largest underground flood control facility, which is designed to reduce rising water levels in four surrounding rivers. Guided tour gave them detailed information about this facility and its functions. This allowed the JDS students to gather information and exchange opinions on the possibility of organized infrastructure development. At Watarase Wetland, the students learned about the reservoir's role in controlling flooding of the Watarase River, which flows around Furukawa City, to improve water quality, provide water for agriculture and domestic use, and conserve wetlands and birds under the Ramsar Convention. They also gathered information on the damage caused by the 2019 typhoon. In addition, the site's former Yanaka Village was the site of eviction during the Ashio Mine Poisoning Incident at the beginning of the 20th century, allowing the group to gather information and exchange views on the pollution movement in Japan. |
| 2022/11/22 | Yokota farm (Ibaraki)    |
The training on food and agriculture was conducted at Yokota Farm. This smallholder business has cultivated rice in Ibaraki Prefecture for several hundred years. After being incorporated as business entity about ten years ago, Yokota Farm has received Emperor's Award and the Minister of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries Award for its good example in small-scale farming businesses. JDS Fellows visited the farm and collected information from Mr Yokota and his wife on farm management, value chain, food education, measures for abandoned land, and agricultural tourism. They were also able to gather information and exchange opinions on methods of preserving and sorting harvested rice, mechanization, and cost reduction. |
| 2022/09/14-09/16 | Osaki Town (Kagoshima)  |
The participants visited Osaki Town in Kagoshima Prefecture to learn about the formation of a recycle-oriented society. It developed a “Osaki System,” in which general waste materials are thoroughly separated, sorted and recycled. The tour included lectures and discussions by Osaki Town environmental officials (including a JICA-supported project for horizontal deployment in Indonesia) and tours of various facilities (final disposal landfill, recycling facility, general waste incineration facility, and resource waste base collection). The participants also learned about town’s policies to promote youth immigration as part of regional revitalization and regional exchange through recycling. On the final day, the participants made presentations on the challenges and strengths of promoting resource recycling in their home countries under the theme of the applicability of the Osaki system to their home countries, and received advice from Osaki Town officials. |
| 2022/09/06-09/08 | Ryukyu University (Okinawa)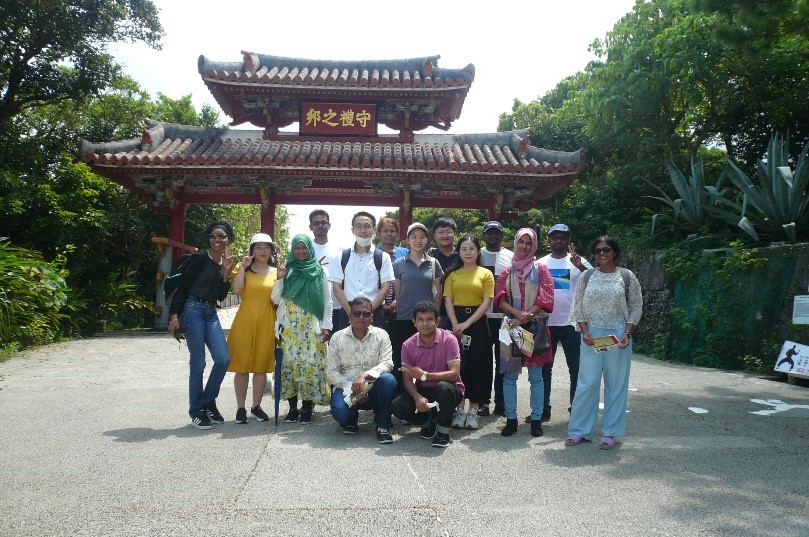  |
The Participants listened to lectures on tropical storms and meteorology by two researchers from Ryukyu University. They visited the Fujukan Museum on the Ryukyu University campus and learned about the relationship between natural disasters and ecosystems. They acquired information about the industry and tourism in the Okinawa Islands through a tour of Shurijo Castle. Based on what they learned, they engaged in group work and deepened their understanding of sustainable development and environmental conservation through presentations and discussions. |
| 2022/08/28-08/31 | Kushiro (Hokkaido)  |
The participants visited the Kushiro Wetland area in Hokkaido to deepen their understanding about marshland ecosystem services, conservation of red-crowned cranes (a national protected species) and rare plants and animals, ecosystem conservation measures through the Old River Restoration Project, and eco-tourism promotion by visiting facilities (Akan International Crane Center, Wildlife Conservation Center, and Kushiro Construction Department of MLIT) and relevant areas. On the last day, the participants presented about the conservation of the Kushiro Marsh ecosystem and lessons learned for environmental conservation, disaster prevention, and industrial promotion in comparison to their home countries. They received advice on their presentations from experts. |
| November/2019 | Kita-Kyushu/Yamaguchi |
This domestic field trip gave our students the opportunity to grasp the latest technological innovations in material recycling and energy recovery efforts in Japan. In Kitakyushu Eco-Town students learned about the integrated recycling complex in the Eco-Town Center and then had the practical visits to the PET bottles and cans recycling facilities. In Yamaguchi Kenraku milk factory the students learned about the fermentation of its organic wastes and by products to produce biogas that is subsequently used to produce steam. The steam is then used as energy input into the milk industry. We also visited Shimonoseki incineration facility and material recovery facility where students strengthened their knowledge about integrated waste management. Finally in Sanyo recycling facility the students could learn about the recycling of fish residue. |
| September/2019 | The Netherlands/Germany |
This field trip aimed to enhance JDS Fellows’ knowledge and insights about agricultural practices, disaster management, and water governance in the Netherlands and Germany. In Amsterdam, the Fellows observed water canals that are important part of city planning and economic development. In Haarlem, the Curuquius museum showed the historic water drainage practices. In Delft, the Fellows observed water drainage practices and dairy farms in polders. They also had seminars with graduate students at the Delft University of Technology. The Fellows then visited the unique storm surge barrier called Maeslantkering at the mouth of the Rhine River (picture) to understand the Delta Work of the Netherlands and the importance of flood protection for the economy. The Fellows then visited Rotterdam to observe the environmental restoration of former development sites and floating forests. They presented about their research topics at the Rotterdam University of Science and Technology and interacted with undergraduate students there. In Germany, the Fellows had a seminar and a short tour about flood management and water governance at the Rhine and the Rhine Commission in Koblenz. Then they went downstream to Cologne for more flood protection practices. |
| June/2019 | China |
This international internship guided the students to study the practices of lake water quality management in Yunnan Province, China. Through this internship, the participants got the first-hand information about the tremendous changes in urban and rural areas in China, especially in Yunnan Province. Being supported by Yunnan University, the students firstly participated in the joint seminar entitled “Pollution Control in Rural Area and Innovative Application of Biomass Energy”. Five students presented their research works and well communicated with Chinese professors and students. During the following days, they visited three lakes at different pollution levels including Fuxian Lake, Xingyun Lake and Yilong Lake, and experienced the changes of the local environment and living conditions of the local people. They also surveyed one village-scale wastewater treatment plant and two national wetland parks where different types of technologies are combined to serve for protecting lake water quality. In addition, the participants paid visits to four historic places such as 17-Hole Bridge and Tuanshan Historic Village, widening their knowledge and understanding of the balance between economic development and environmental protection. This internship not only provided a good chance for the participants to understand the environment and sustainable development, but also help them to seek efficient solutions for lake pollution issues. |
| January/2019 | Kushiro(Hokkaido) |
With sustainable management of Kushiro Wetland as a core topic, students learned about conservation and utilization of natural resources for economy and tourism, river restoration, and endangered wildlife conservation in the Kushiro Wetland area through site visits, lectures and discussion by local experts. |
| December/2018 | Kita-Kyushu/Yamaguchi |
Students visited Eco Town Center in Kita-Kyushu City and received an overview of the Eco Town project including all the recycling initiatives. The main goal of Eco-towns in Japan is to design a recycling-oriented society where wastes in one sector can be used as raw materials in other industrial sectors. After the Eco Town visit, the students visited a biomass facility in Arao city. On the following day, the students visited facilities to make effective use of biogas and methane gas and received explanation about the relationship between region and industry in waste recycling. |
| November/2018 | Malaysia |
Students participated in the 10th Better Air Quality Conference 2018 (International Conference on Air Quality Improvement) in Kuching, Malaysia. Students learned about the current state of atmospheric environmental problems in developing countries, mainly in the Asian region, and the concepts and efforts concerning air quality management technology and policies. In addition to gaining knowledge listening to lectures and presentations by experts, the students nurtured their problem recognition ability and international communication ability through communicating with the participants at the conference sessions. |
| September/2018 | Okinawa |
This field trip is designed to examine the challenges and possibilities of developments in Okinawa. This area has been one of the most popular tourism destinations in Japan with rich cultural, environmental, and historical heritages. FOCUS: (1) the conservation of local ecology and marine ecology; (2) a historical study about the establishment of Ryukyu culture and impact of World War II on the local environment and economy; (3) historical roots of Japanese-Okinawan relations; and (4) possibilities of future tourism in remote areas |
| July/2018 | Liverpool(UK) |
Visit Liverpool, UK, learn about Mercy River campaign, the pioneering environmental symbiosis city policy in the world. Students learned about water management policy and urban development centering on rivers and considered policy application to their country while comparing their case. |
| May/2018 | China | This international internship to China consisted of three parts. (1) Beijing internship: Field trip to Xiaojiahe Wastewater Treatment Plant (Beijing) and the China-Japan Joint Seminar on Water Environment Technology in Tsinghua University. (2) Tianjin internship: Field trip to the Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city and the Symposium on Technological Innovations in Environmental Control and Resources Recovery & Utilization in Nankai University, Tianjin. The two field trips are related with environmental issues and applicable technologies in China, through which the students can know how people are trying their best to make their surroundings more beautiful and sustainable. During the seminars, the students had good chance to communicate with the young generation of scientists and specialists who are contributing themselves to environmental protection and sustainable development in China. (3) 2018 International Students Conference on Environment and Sustainability (ISCES) hosted by the UNEP and Tongji University. The students were offered great opportunities to exchange ideas on the environment and sustainability regarding plastic wastes with fellow students from more than 30 countries. The students also actively participated in the intensive lectures, group discussions, field trips to rural and urban areas, and poster competitions. |
| February/2018 | Kushiro (Hokkaido) |
On the theme of sustainable natural resource utilization, students learned about natural revitalization, tourism use of Kushiro Wetland, rare wildlife conservation in Kushiro Marsh, historical cultural background of nature management, and hotel management using waste heat and agriculture among other topics. |
| February/2018 | Okinawa |
JDS students learned the influence of overuse and climate change on coral reefs, the cultural formation of urban landscape in Okinawa, and the relationship about agriculture and regional promotion. With the cooperation of the University of the Ryukyus, we had the opportunity to attend lectures of researchers at the university and learned the latest research results. |
| February/2018 | Tsukuba (Ibaraki) | Students visited the Center for Genetic Resources, Gene Databank and Agricultural Environment Change Research Center in the Agricultural Research Organization, and learned the latest knowledge on genetic resource recording, preservation technology and soil carbon storage research through lectures and facilities tours. |
| January/2018 | Tokyo | This year JDS students together with 6 professors joined this domestic trip which mainly consisted two activities: (1)visiting to the National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation; and (2)surverying the Tokyo bay, especially Odaiba, Hinode, and Asakusa areas. All the participants experienced the advancement of technologies for environmental managemnet in Japan, especially on surface water systems and waste disposal, which is beneficial for the students to obtain the real ideas of betterment of the environment. |
| December/2017 | Kita-Kyushu/Yamaguchi | This trip gave students to learn about the importance of industry-government-city collaboration regarding environmental management. In the visit to Kitakyushu Eco Town we learned about the technologies to recycle PET bottles and Al and Steel cans. We also visited Yumoto biomass boiler that supplies hot water to a hotel by using only wood chips as fuel. We had the opportunity to visit Yamaguchi Dairy industry biogas plant. This plant uses the byproducts and wastes from the dairy industry combined with sludge form the local wastewater treatment plant and produces biogas that is used as a source of energy in the dairy industry. Finally we visited a food waste recycling plant u\in Ube city. The plant uses the food wastes from super markets, convenience stores, hotels, etc to produce animal feed. From these field studies students understood the importance of having a life cycle thinking regarding resource management. |
| August/2017 | Mongolia | This international internship mainly consisted of three activities. (1)Paid a visit to the rural area of Ulaanbaatar where the participants acknowledged the history of Monoglia and her development issues. (2)Parcipated in a seminar co-organized by the Ulaanbaatar City Government and University of Tsukuba, in which all the partipants presented their research works and findings. Through this seminar, the participants well communicated with the local government officials who are expecting to learn and contribute more to the development of Ulaanbaatar. (3)Visited the central wastewater treatment plant and sampled the typical sludges which were further used for identification of the efficient bacterial species. During this internship, the participants also visited one solar energy demonstration building where the participants exchanged ideas with the local officials who are in charge of this system. This internship can help the participants understand more about Mongolia and its environmental problems. |
| March/2017 | Ibaraki | JDS Fellows and SUSTEP students visited Shimizu Farm and learn about small/medium sized farm management, soil production, and larger agricultural concepts from Mr Shimizu. |
| January/2017 | Okinawa | JDS Fellows and SUSTEP students learned about desalination technologies, wetland conservation, coastal development and historical conflicts. |
| January/2017 | Tokyo | JDS Fellows and SUSTEP students visited the water supply museum in Tokyo. They also observed super levee development areas along the Sumida River to better understand Tokyo's water management policies and disaster management. |
| December/2016 | Tokyo |
JDS Fellows and SUSTEP students visited the solid waste treatment system in Tokyo at the Central Breakwater Intermediate and Final disposal facilities and sites. They learned about recycling technologies and future waste management problems in Tokyo. |
| October/2016 | Tokyo | JDS Fellows visited the Central Breakwater Outer Landfill site in Tokyo Bay. First, the Fellows received a short lecture from the Tokyo Metropolitan government about its waste management history and current practices. Then they observed the intermediate waste processing facilities and learned about what technologies are available to process and recycle wastes. Finally, they visited the final disposal site and observed such technologies as sandwich methods, leachate water collection and treatments, and biogassification from methane collected from this site. |
| September/2016 | Ulaanbaatar (Mongolia) |
The Fellows participated in the seminar on urban environmental improvement, which was organized by the University of Tsukuba and hosted by the City of Ulaanbaatar. Researchers from the National University of Mongolia were also invited as speakers. The topics focused on remediation, especially as it is related to soil and water contamination. On the second day, the Fellows had excursion to actual contaminated sites, and learned about some specific plant species that tend to absorb heavy metals. Ulaanbaatar City employees guided the Fellows and our professor to the Ger area where soil pollution is most obvious. |
| August- September/2016 |
The Netherlands |
The Fellows participated in the joint seminar between the University of Tsukuba and the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands. On the first day, the Fellows spent a few hours to discover the roles of the intricate canal system in Amsterdam historically. On the second day, they moved to the town of Delft and had a tour from a Delft University of Technology professor about how waterways played important roles in the development of this city. On the following day, the Fellows participated in in-class seminar and listened to lectures by Delft University of Technology professors and doctoral students about disaster prevention, green development of cities, and water management. In the afternoon, the Fellows made presentations about environmental issues in their countries and exchanged ideas with researchers at Delft. On the fourth day, a representative in urban planning from the Rotterdam government came to present Rotterdam's urban planning and disaster prevention efforts. In the afternoon, the Fellows were guided by this person to the Rotterdam area and observed on-going redevelopment plans in the city. On the fifth day, the Fellows visited and had a lecture at Maeslantkeringweb, the large storm surge barrier. They collected information about the Netherlands Delft Work and technologies to save ports from storms and floods. Afterward, the Fellows visited one of the largest intensive agricultural complexes in Europe called "Westland." Here the Fellows learned about green house agriculture and traditional water routes to transport agricultural goods. The Fellows overall learned about disaster management, water management, urban/regional planning, and agricultural efficiency. They chose one topic and wrote a report by comparing issues in their own countries. |
| June/2016 | Ashio (Tochigi) | JDS Fellows visited the Ashio valley, the former copper mining site. Here they learned about the impact of copper mining on the valley environment, especially at the former neighborhood of Matsuki. They also observed some remnants of advanced industrial developments in the town, including the Japan's first hydroelectric dam site, iron bridges, and mine technologies. From a guide who grew up in Ashio, the Fellows learned about social life of Ashio in the mid-twentieth century. Another important aspect of this trip was to observe the forest restoration efforts in the Valley by volunteers. The Fellows could learn how once devastated valley became covered with green areas and brought back some wildlife such as bears, deer, and monkeys. The Fellows wrote their reports on the history of Ashio in comparison with issues in their own countries. |
| May- June/2016 |
Shanghai (China) |
The major SUSTEP consortium universities including IPB (Indonesia), NTNU (Taiwan), Fudan University (China), Tongji University (China) and CUG (Beijing, China) participated in the International Symposium on Education and Environmental Sustainability held in Wuxi, Jiangsu Province, China during May 31 to June 1. Together with the professors, the JDS fellows had a good communication with the students from these universities concerning environmental education, development of sustainable technologies and policies. All the follows visited the Taihu Lake which is suffering from algae and water environment deterioration problems, where they also witnessed the changes after effective and sustainable technologies being applied. On June 2 the fellows had a field trip to a dairy farm where a large-scale biogas plant has been constructed and operated to deal with the dairy manure and wastewater, and recover energy as biogas (methane) as well through an environmentally-friendly way. During June 3 to June 8, the fellows took part in the 2016 International Student Conference on Environment and Sustainability (ISCES). They surveyed the Chongming Eco-island and several typical places in the center area of Shanghai, and experienced the vast changes after urbanization by themselves. Besides, intensive seminars and competitions among the international participants were conducted regarding Sustainable Community Space and Green Lifestyle. |
| January/2016 | Okinawa |
JDS fellows joined the field trip to the main Okinawa Island and engaged in hands-on sugarcane harvesting activity and brown sugar making. They also learned about the Karst environment and marine ecosystems in connection to distinctive Okinawan culture and history. On the final day, they visited the Ramsar site and observed the expansive wetlands in urban areas. An expert on Okinawan traditional language and culture, Shisei Toma, was invited to give lecture about history and culture of Ryukyu people. The Fellows also visited some politically controversial environmental problems in Okinawa such as the Futenma Replacement Facility plan at Henoko Bay. |
| December/2015 | Tokyo |
In the morning, in collaboration with Tokyo’s Bureau of Environment, JDS Fellows received lecture about waste management of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. They received information about garbage collection, processing, and final disposal processes. The Fellows then visited garbage processing facilities and final disposal site called the Central Breakwater Outer Landfill Site. They learned about the future plans of waste disposal and various ways to maintain solid waste safe from environmental contamination. In the afternoon, the Fellows took a water taxi and observed Tokyo’s “super levy” project and other river management areas in the Sumida River. |
| October/2015 | Tokyo |
JDS Fellows had small seminars about eco-town projects in Tokyo at the Metropolitan government building. They acquired knowledge about waste management and urban planning for eco-cities. The Fellows also visited the office of the Japan International Cooperation Center and exchange ideas about the future outlook of JDS alumni associations. |
| September/2015 | Izu/Shimoda (Shizuoka) |
This trip attempted to better understand rural development (e.g., community-based tourism) and the marine environment. The Fellows visited the University of Tsukuba's Marine Research Center and observed some of its on-going research projects. They had a small seminar about geoparks. Dogashima cruising allowed them to observe the formation of unique geological features. In Toi, the Fellows learned about the mining operation and tourism development at the former mining site. They also received a lecture about the early contact history in Shimoda between Japanese and Americans at Ryosenji Temple. |
| September/2015 | Ulaanbaatar (Mongolia) |
JDS Fellows and JDS graduates presented their research topics that are related to urban environmental problems in Ulaanbaatar. This seminar was hosted by Ulaanbaatar City. They exchanged ideas about the future cooperation efforts with the city. The Fellows then visited City's waste treatment plant and Ger areas to better analyze the conditions. |
| July/2015 | Hanoi (Vietnam) |
This seminar was conducted in collaboration with the Hanoi University of Natural Resources and Environment (HUNRE) and the Delft University of Technology. The aim was to analyze water problems and find some possible solutions. JDS Fellows acquired knowledge about urgent water problems in Hanoi in two-day seminar. They also spent one day in the field, observing and collecting data about water problems. |
| June/2015 | Ashio (Tochigi) |
JDS Fellows visited the former Ashio copper mine site. Former residents and guides showed them to important industrial achievement during the thriving period of mining operations. The Fellows also observed reforestation activities in the Ashio valley. At the Ashio History Museum, they acquired knowledge about the history of mining technology and the emerging environmental activism. |
| June/2015 | Shanghai (China) |
This international internship was carefully designed with the combination of an international student conference (2015 International Student Conference on Environment and Sustainability) with two additional days' field trip particularly focused on applicable technologies and management systems of waste and wastewater treatment in China. This activity was co-organized by Tongji University (China).The Fellows learned how to use different treatment technologies to cope with different organic solid wastes and wastewaters, making full advantages of these wastes to benefit local people. |
| March/2015 | Kasumigaura (Ibaraki) |
This trip introduced JDS Fellows to some major economic activities in the water environment around Kasumigaura Lake, Japan's second largest lake. They observed lotus root harvesting and other wetland crop cultivations. They visited the former water town, in which elaborate canal systems developed, and only boats were used for transportation. Then they observed the recent road and bridge works around the lake. |
| February/2015 | Watarase Yusuichi (Chiba) |
As the only Japan's artificial wetland to be protected under the Ramsar Convention, Watarase wetlands functions as flood control, water purification, and water supply reservoir. The area also includes the Yanaka village site, which was forcibly closed due to copper pollution from the Ashio mine in the beginning of the twentieth century. The Fellows learned about both history and current scientific practices here. |
| January/2015 | Meiji Gakuin University |
With renowned environmental/disaster law expert from the University of California, Berkeley, JDS Fellows went to Meiji Gakuin University for a seminar. At this seminar they learned about disaster law that pertained to large-scale pollution. The Fellows also exchanged ideas with faculty members at Meiji Gakuin to expand their academic capacity. |
| December/2014 | Tokyo |
This trip aimed to acquire knowledge about community-based management in urban settings. The Fellows visited the Fukagawa History Museum, which is one of the successful and earliest attempts in Tokyo by community to protect and promote local culture and history. They also visited the Ainu Cultural Center near Tokyo station, where some Ainu cultural exhibitions helped Fellows better understand the importance of establishing cultural center in urban areas. |
| September/2014 | Kyushu University |
The Fellows had 5 days' trip in Minamata including full field work, lectures and group working in order to answer the question "Why has Minamata not been solved yet?" which was initialled by Kyushu University. They visited Soushish Museum of Minamata disease, Chisso Company, Hotto House where the fellows interviewed some patients of fetal Minamata disease, uncertified patients in Amakusa Island, etc. Finally they directly exchanged ideas with the Mayor and officials of Minamata city Government. Through this trip the Fellows experienced how Japanese people dealt with and are dealing with the real environmental issues. |
| September/2014 | Nagano |
This fieldwork was conducted in the primary forest region of Buna trees in northern Nagano prefecture primarily to understand forest ecology and rural/regional development. Students interacted with local foresters and farmers to understand economic and social issues they face today. Students also participated in one of distinctive local autumn festivals in Iiyama City and learned about Japanese religious culture. They lodged in one of temples, which serves as various social functions, including forest therapy for cancer patients. |
| August/2014 | Ulaanbaatar (Mongolia) | JDS Fellows and graduates presented their research topics to Mongolian people, including those who might be interested in the JDS Fellowship. The presentations focused on urban environmental problems in Ulaanbaatar City and environmental-policy related topics. The Fellows also visited Ulaanbaatar City and met Vice Governor in charge of environmental issues, and exchange ideas about urgent environmental problems in the city. |
| August/2014 | Hanoi (Vietnam) | JDS Fellows and graduates presented their research topics to Vietnamese people, including those who might be interested in the JDS Fellowship. The presentations focused on environmental policies, climate change, and disaster management. The Fellows also visited the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment and its Vietnam Environmental Agency and a few agencies to acquire knowledge about urgent environmental issues for Vietnam. |
| July- August/2014 |
Okinawa |
JDS Fellows in Environmental Sciences and those Fellows in Social Sciences and Humanities had a joint field trip to Okinawa. They acquired knowledge about the history and culture of the main island as well as some on-going problems of military base replacement debates in Futenma and Henoko. |
| July/2014 | Kyoto/Nara | In Kyoto and Nara JDS Fellows observed various types of Japanese forest management, including "biotope" forests that were established to enhance biodiversity conservation. They also observed historical forest management practices at the end of the sixteenth century. A short seminar was offered to better understand reforestation and the forest's resilience. |
| February/2014 | Hiroshima/Miyajima |
This study excursion introduced JDS Fellows to some salient aspects of Japanese culture, history, the urban environment, environmental management, and tourism in Hiroshima city and Miyajima. In Hiroshima, visits at Hiroshima castle, medieval garden, Atomic Bom Dome, Peace Memorial Park/Museum enhanced the understanding of changes in the urban environment, tourism, green/public space before and after World War II. Fellows also had a grasp of the history of the impact of Atomic bomb on the city by looking at museum exhibition and surviving trees as well as the significance of maintaining cultural and historical heritage for public environmental education. In Miyajima, Fellows visited ancient forests and the rare colony of coniferous trees to investigate distinctive vegetation/ecological features in the national park. Also, they visited world heritage site and saw important roles cultural heritage sites play in managing national parks as well as sustaining local businesses, including tourism. |
| February/2014 | Sapporo |
During this trip the students visited Hokkaido University. Because of the snowy weather, they cancelled the outdoor activites and mainly visited the School of Engineering and the Graduate School of Environmental Science. They attended two meetings and one seminar in Hokkaido University and had a good communication with the professors, researchers and students. The students also gave a research presentation in the seminar. From this trip they learned that Sappora has been beset by four major water/ wastewater issues: arsenate in source water, heat energy recycling from wastewater treatment, snow issue and water reuse in urban area. They also knew how these issues were solved one by one by the Japanese researchers and engineers. In addition, the students learnt some new technologies which are promising for the removal of radioactive Cs from contaminated soil. Through this trip a mutual communication between Hokkaido University and Unversity of Tsukuba has been established. |
| December/2013 | Tokyo |
Visited Tokyo and learned about urban greening. It was a meaningful experience for JDS fellows for their research to learn about historical context of the land and the social mechanism. |
| November/2013 | Kobe(Hyogo) | Visited the Kobe water quality test site, to obtain a better understanding of water quality management and safety management of drinking water in Japan. It would be the thing that is very helpful to the safety management of the drinking water of Mongolia in the future. |
| October/2013 | Tokushima University | Visited Tokushima and learned effects of water environment of the underground. It was possible to obtain a meaningful knowledge regarding environmental facilities and land price data. It is considered that would be able to contribute to the future development of Ulaanbaatar city. |
| September/2013 | Oze (Gunma) |
Observed wetland convervation and identified typical wetland vegetation at Ramsar designated Senjogahara of Nikko and Oze National Park. At Oze National Park, we interviewed local people and collected information about access control to the national park as well as recent trends of tourists. |
| September/2013 | Shinshu University (Nagano) | Attended the climate system seminar on "radiative balance and climate sensitivity," which focused on climate formation. Also acquired information about the winter monsoon and the relationship between vegetation and snowfall. The data were based on field research. |
| July/2013 | Bandung (Indonesia) |
Attended the Pacific Conference of the Regional Science Association International in Bandung. The conference helped find out about the latest research on regional science and regional development policies. Students also visited some historical and natural places related to the environmental issues. |
| June/2013 | Fukuoka (Kyushu) | Visited the JICA Kyushu office and exchanged views and information about the current state of nature conservation projects in Mongolia within an ODA scheme. Also, visited the Sanctuary of pyroclastic flow trace of Fugen ,and learned about damage mitigation and disaster prevention measures. |
| June/2013 | Miyake-jima (Izu Islands) |
Observed the forest ecosystem recovery process after the 2000 eruption
of Miyake-jima. Student learned about the recovery response of forest ecosystems
to the huge disturbance at local monitoring sites. And also examined on-going vegetation survey methods and measuring ecosystem functions. |
| June/2013 | Memanbetu (Hokkaido) |
Visited Shiretoko National Park and collected information about eco-tourism. Students learned about the surveying practice for ecosystem restoration in Salicornia wetlands in natural forests around the campus of the Tokyo University of Agriculture at Okhotsk. This visit helped understand the challenge for ecological restoration. The two JDS students made research presentations, and exchanged views on issues surrounding the natural environment of Vietnam and Mongolia. |
| February/2013 | Shanghai (China) | Visited water treatment facility and waste management in the city to understand Chinese efforts for establishing recycle oriented society. |
| February/2013 | Ise-Shima National Park (Mie)  |
Visited Ise-Shima National Park to understand how the Park has been conserved by shrines and local peoples despite 90 percent of the park is privately owned. Students collected information about how Japanese religious culture affected the conservation of forest resources. They also visited Pearl Island in Shima, where the world’s first cultivation of pearls became successful. The island became one of important tourism resources in the area, providing environmental education. |
| January/2013 | Izumi (Kagoshima) | Observed how wildlife conservation, especially cranes, has been undertaken by the Crane Museum in the city. Mongolian student made a presentation about Mongolian crane preservation and the protection of its nursery habitats. |
| January/2013 | Hitachi-oomiya (Ibaraki) | Observed some problems Japanese rural areas are facing, including de-population, abandoned farm lands, the promotion of local businesses and resettlement. These problems can be similar to what may happen in developing countries. |
| November/2012 | Yokohama (Kanagawa) | Students participated in the Eco-balance Conference. They presented their research in progress. |
| September/2012 | Tokyo (Tokyo)  |
Students and one visiting professor from Australia visited the Ainu Cultural Center in Tokyo to find information about the promotion activities of Ainu peoples in the Tokyo area. They also visited the restoration of forests in the Meiji shrine area along with the successful creation of sacred site there with the shrine in the heart of Tokyo City. |
| August/2012 | 1. Ashio 2. Watarase Artificial Wetland (Tochigi) |
1. Visited the former copper mine sites and factories that caused environmental problems in the valley in the beginning of the twentieth century. This led to the first environmental litigation in Japan. 2. Visited Watarase Artificial Lake that was designated as one of Ramsar sites in July 2012. Some parts of this area was considerably affected by the toxic run-off from the Ashio mine in upper stream. |
| July/2012 | 1.Kasuga Old-growth Forests (Nara) 2.The Higashiyama Mountains (Kyoto) |
1.Visited the old-growth forest at Kasuga and observed how the forest has been kept intact and how temple/ shrine-owned forests have played roles in conservation of the forest. 2.Observed the spreading problems of dying trees in the Higashiyama Mountains and learned about restoration efforts. |
| July/2012 | Kushiro Wetland | Visited the Kushiro area to collect information about wetland management. |
| February/2012 | Naoshima and Teshima (Okayama) | Visited these two islands in the Seto Inland Sea National Park to learn about industrial waste disposal problems. Students also observed how local people promote tourism and local industries. |
| December/2011 | Miyakojima(Okinawa) | Visited one of the world’s largest underground dams to learn about water management technologies that are used by the local community. Students carried out a field survey of the structure of the dam. They learned also about the rationale behind its construction and the state of groundwater. |
| June/2011 | Sapporo, Nibutani, Shiraoi (Hokkaido)  |
Visited Ainu cultural centers and national parks to understand the cultural significance of ecosystems in Hokkaido. Students also examined the state of hydroelectric dam in Nibutani, which affected several culturally significant sites and Ainu rights. In Sapporo, they observed one the oldest Ainu embroidery classes in Japan. Report (June 2011, Hokkaido) |
| February/2011 | Beppu (Oita) | Visited waste water treatment and biomass energy collection facilities to seek for feasible models in establishing recycle-oriented society that may produce food packaging materials and fuels from wastes. Students observed current Japanese recycling technology. Organized in collaboration with the Waste Management Expert Course (G30). |
| Okuizumo (Shimane) | Observed industrial promotion and environmental conservation in remote mountains and hill-side regions. The activities included a visit to the World Heritage site at the former Iwami silver mine. | |
| Kushiro(Hokkaido) | Examined the livestock industry. The purpose was to compare the large-scale livestock industry in Japan with that in Mongolia. | |
| July/2010 | Tunisia | Students joined the international internship of the Environmental Diplomatic Leader (EDL) education program to explore water and public health issues in Tunisia. |
2. Theses
2022
- Enkhbold Bayarmaa “Policy Implementation and Community Participation in Urban Green Space Development in Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia “ (モンゴルのウランバートル市における都市の緑地化に関する政策履行とコミュニティー参加について)
- Chinbat Enkhchimee “Characteristics of Soil in the Surrounding Areas near the Low-Grade Copper Ore Dump in Mongolia “ (モンゴルにおける低品位銅鉱石廃棄地周辺の土壌の特徴)
- Dashtogtokh Tumurtsooj “Evaluation of Water Quality by Using Hydrological Data in Selenga River Basin, Mongolia “ (モンゴル国セレンガ川流域における水文データを用いた水質評価)
- Gansukh Davaajav “Stakeholder’s Perception of Challenges on Ger Area Re-planning Policy in Ulaanbaatar City of Mongolia “ (モンゴル・ウランバートル市のゲル地区再開発政策についての利害関係者の認識に関する研究)
- Shajbalidir Amarbileg “Assessment of Groundwater Quality in the East Gobi Basin, Dornogobi, Mongolia “ (モンゴル国ドルノゴビ県東ゴビ盆地における地下水水質評価)
2021
- Batdelger Uranchimeg “GIS-based Identification of Potential Optimal Locations for Disposal of Radioactive Waste in Mongolia“ (GISを用いたモンゴルにおける放射性廃棄物処分の最適候補地の特定)
- Enkhtur Munkhbat “Hydrothermal Treatment of Rice Straw for Carbohydrate Production“ (炭水化物生産のための稲わらの水熱処理)
- Geserbaatar Nandin-erdene “Estimation of the Above-ground Biomass and Carbon Stock in Boreal Forest Using Satellite Data with Machine Learning“ (衛星データと機械学習を用いた寒帯林の地上部バイオマスと炭素蓄積量の推定)
- SURENJAV BUYANDELGER “Anthropogenic Impact on Water Quality of Tuul River, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia“ (モンゴル・ウランバートルのトゥール川の水質に及ぼす人為的影響)
2020
- BAYARSAIKHAN UNDRAKH “Accuracy Assessment of the Vegetation Indices Derived from the GCOM-C Satellite in Mongolian Grassland“ (モンゴル草原における人工衛星 GCOM-Cから得られた植生指数の精度評価)
- Dashdendev Munkhbadral “Promoting Sustainable Mining in Mongolia: Identifying Current Policy Gaps“ (モンゴルでの持続可能な鉱業の促進:現在の政策ギャップの特定)
- Tsevegjav Boldbaatar “Examining Green Building Development Trends and Prospects in Mongolia: Case Study of Office Spaces in Ulaanbaatar City“ (モンゴルにおける環境不動産開発の動向と今後の課題に関する研究:ウランバートル市のオフィス賃貸を対象として)
- Ulziibaatar Munguntuul “Using Herders’ Traditional Knowledge to Conserve Rangeland in Murun Soum, Mongolia“ (モンゴルのムルン郡において牧草地を保全するために遊牧民の伝統知を利用する研究)
2019
- Baasankhuu Nyamsuren “Backscattering Analysis of GPM Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar for Vegetation Detection in Mongolia”
- Enkhbaatar Davaanyam “GIS-based Analysis of Air Pollution Mechanism in Ulaanbaatar City: Air Quality Improving Measures”
- Jambaldorj Bayarmagnai “Analysis of Particulate Matter (PM10) Emission Sources in Non-heating Season in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia”
- Khurelbaatar Undarmaa “Analysis of Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Potentials in Mongolia through Carbon Mechanisms: Case of Energy Sector”
2018
- KHURELBAATAR JAVKHLAN “A Policy Study on Sustainable Urban Development of Ulaanbaatar City”
- NARANBAT NASANJARGAL “A Study on Air Pollution Reduction Policy in Ulaanbaatar City through the Promotion of Solar Heating System”
2017
- Gan-Ochir Davaajargal “Evaluation of the Cost and Benefit of Adopted Air Pollution Strategies in the Ger Area, Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia”
- Shagdarsuren Chantsalnurmaa “A Study on Possibilities of Green Development to Solve Environmental Pollutions in Ulaanbaatar City: A Case Study on Eco-district”
2016
- Enkhbat Oyuntselmeg “Enhancing Eco-standardization Policy for Public Bathhouses in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia”
- Enkhbold Bayarmaa “A Study on Urban Parks Accessibility to Improve Current Urban Parks Planning and Management in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia”
2015
- Odgerel Dalkhjav “Evaluation of Environmental Impacts of Tannery Effluents in Tuul River with Water Quality Index (WQI), Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia”
- Galdnaa Munkhzul “Study on the Violation of Norm of Urban Planning in Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia”
2014
- Erdenebadrakh Munkhjargal “Snowfall Variation in Mongolia and its
Relationship with Atmospheric Circulation” - Nurymkhan Marjangul “Biological Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium and Mechanism Analysis of Detoxification by Enterobacter sp. HT1 Isolated from Tannery Effluents, Mongolia”
- Budjav Khishigjargal “Hedonic Analysis of Land Prices Focusing on Urban
Amenities: A Case Study of Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia”
2013
- MUNKHUU, Undraa “Succession and Regeneration of Pseudo-Taiga Larch Forests After Fire in Tarvagatai Mountain Range, Mongolia”
- YADMAA, Tseveenkhand “Environmental Management through Tourism in Khan-Khentii State Special Protected Area, Mongolia”
- BADAMSED, Delgermaa “Impacts of Herder Livelihood on Waterbird Habitats in Mongol Daguur Strictly Protected Area and its Buffer Zone and Possible Solutions for Wetland Ecosystem Conservation”
- GANTUMUR, Tuvshinjargal “The Integrated E-waste Management System in Mongolia : Learning from the Experience of Developed Nations”
2012
- Gonchig, Gantulga “The Establishment of Sustainable Livestock Farming Service in Galshir, Mongolia: Challenges and Possibilities of Integrated Governance.”
- Nyamsambuu, Khishigsuren “Optimal Pastureland Use Planning in Bayan, Mongolia using Remote Sensing and GIS.”
- Natsagdorj, Natsagsuren “Evaluation of factors affecting on soil moisture in semi-arid regions in Mongolia.”
2011
- Zagdragchaa, Otgonbayar “Cycle-oriented Environmental Study in Hide and Skin Processing Factory: Removal of Chromium from Tannery Wastewater by Adsorption onto Cost-effective Material.”
2010
- Dolgorsuren, Saruul “Pasture Resources Use by Nomads of Mongolia and the Necessity of Sustainable Regulation: The Case of Lake Hövsgöl.”
- Lamjav, Oyunjargal “Inter-annual and Inter-decadal Variation of Precipitation and Its Influence on Pasture Production in Mongolia under Ongoing Global Warming.”
2009
- Tsolmon, Namkhainyam “Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emission of Mongolia: Input-Output Analysis.”
3. Message from Past JDS Fellow
|
 |
I would like to express my earnest appreciation to the governments of Japan and Mongolia for arranging this scholarship program in support of human resource development in Mongolia. Also, I need to express my sincere gratitude to the University of Tsukuba, especially those professors who guided me in field of environmental sciences.
The University provides us with a whole range of new technological facilities to support our study and research activities. In addition to having a great mentor, I had a lot of opportunities to meet and learn from leading scholars based in Japan and abroad. All the opportunities helped me develop new insights, applied knowledge, and practical skills. The two years at the University enriched my life personally and professionally. One thing I would like to advise new JDS fellows is that there exists no upper limit for acquiring course credits. So, use this chance, and attend as many classes as you want.








